
Laws of reflection — lesson. Science State Board, Class 8.
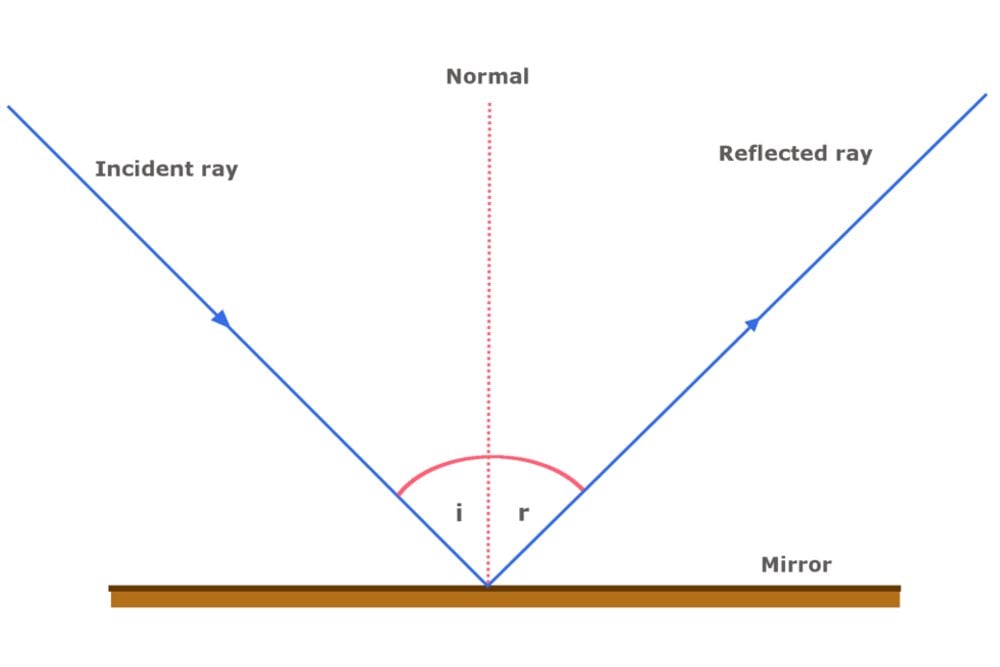
The law of reflection is illustrated in Figure 1.3.1 1.3. 1, which also shows how the angle of incidence and angle of reflection are measured relative to the perpendicular to the surface at the point where the light ray strikes. Figure 1.3.1 1.3. 1: The law of reflection states that the angle of reflection equals the angle of incidence—θ r.

what are the laws of reflection? explain with diagram Brainly.in
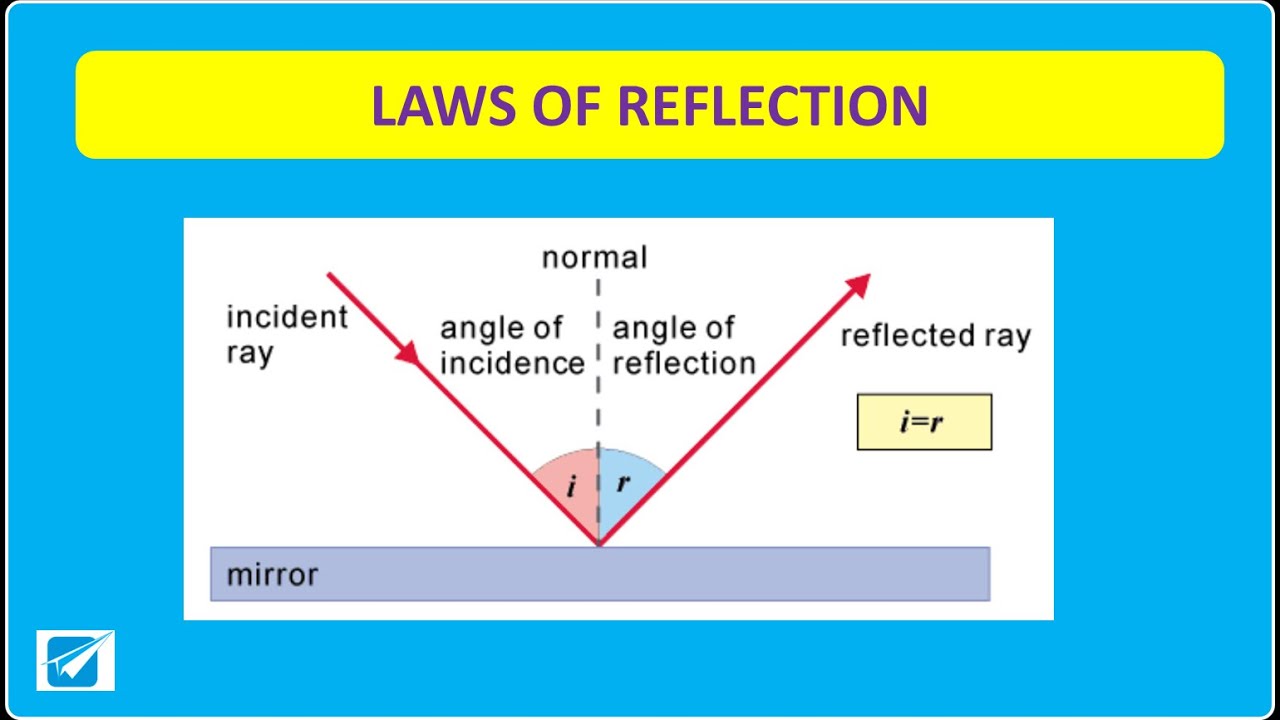
The law of reflection states that the angle of reflection equals the angle of incidence— θr = θi. The angles are measured relative to the perpendicular to the surface at the point where the ray strikes the surface. Figure 2. Light is diffused when it reflects from a rough surface.
Specular and Diffusion ReflectionHow Light Reflects MooMooMath and
Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\): The law of reflection states that the angle of reflection equals the angle of incidence—θ r =θ i. The angles are measured relative to the perpendicular to the surface at the point where the ray strikes the surface. We expect to see reflections from smooth surfaces, but Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\) illustrates how a.

PPT Unit 3 Light and Optical Instruments PowerPoint Presentation
Large telescopes use reflection to form an image of stars and other astronomical objects. Figure 25.2.1 25.2. 1: The law of reflection states that the angle of reflection equals the angle of incidence -- θr = θi θ r = θ i. The angles are measured relative to the perpendicular to the surface at the point where the ray strikes the surface.

LAW OF REFLECTION YouTube
The law of reflection states that the angles of an incident ray and reflected ray are the same as each other and are in the same plane as the normal. The law describes the behavior of light reflecting off of a very smooth surface. This is specular reflection or regular reflection. In contrast, diffuse reflection occurs from an irregular surface.

Reflection of Light Definition, Types, Laws & More Leverage Edu
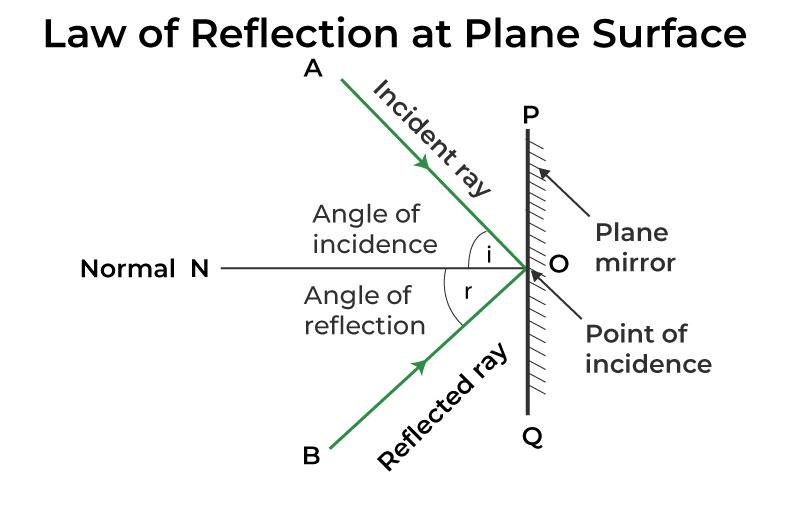
There are two laws of reflection: 1) The incident ray, reflected ray and normal lie on the same plane. 2) Angle of incidence is equal to angle of reflection. In case you are referring to the first law,to some extent yes it is imaginary because a plane is a human made concept ( does not have any physical existence) but it is nevertheless important.

Reflection of Light Definition, Types, Laws & More Leverage Edu
Law of Reflection Specular vs. Diffuse Reflection Light is known to behave in a very predictable manner. If a ray of light could be observed approaching and reflecting off of a flat mirror, then the behavior of the light as it reflects would follow a predictable law known as the law of reflection.
Laws of Reflection Definition, Types, Formula, Uses, & FAQs
Laws of Reflection is a principle or rule that governs the phenomenon of reflection of light. The law of reflection states that a light ray will reflect off a surface at the same angle that it hit it when it comes into contact with it.
7 LAWS OF REFLECTION YouTube
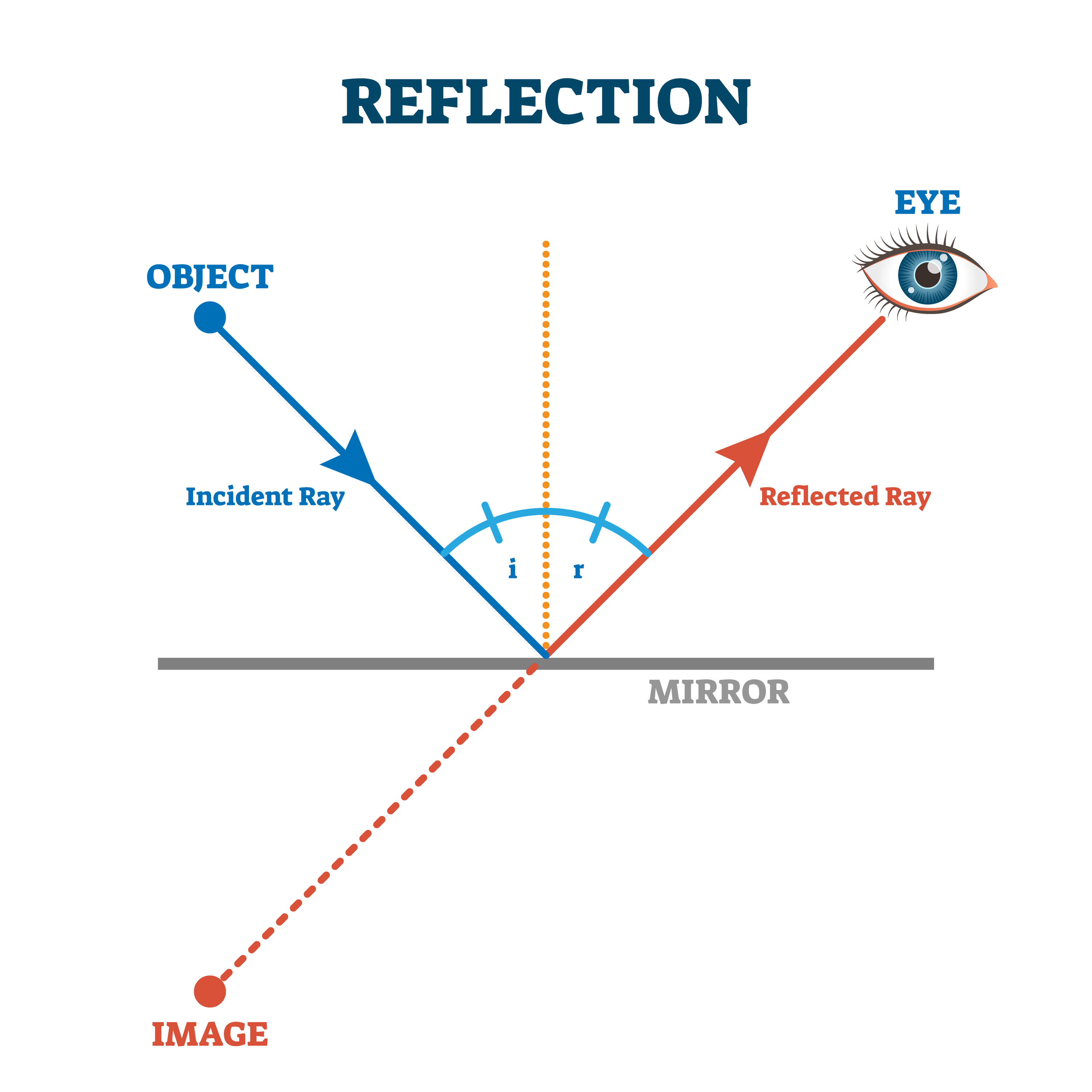
The Law of Reflection The angle of reflection equals the angle of incidence. When we see ourselves in a mirror, it appears that our image is actually behind the mirror. This is illustrated in Figure 6. We see the light coming from a direction determined by the law of reflection.

Reflection of Light Definition, Types, Laws & More Leverage Edu
Laws of reflection are: (i) The incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal ray at the point of incidence, lie in the same plane. (ii) The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection. Table of Contents show What is reflection and Refraction class 10th?
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/ReflectionLaw-5946c6dd5f9b58d58a2f2efc.png)
How Reflection Works in Physics
The law of reflection states that the angle of reflection equals the angle of incidence— θr = θi. The angles are measured relative to the perpendicular to the surface at the point where the ray strikes the surface. Figure 2. Light is diffused when it reflects from a rough surface. Here many parallel rays are incident, but they are reflected.

4.2 The Law of Reflection Douglas College Physics 1207
Figure 1.7 (a) When a sheet of paper is illuminated with many parallel incident rays, it can be seen at many different angles, because its surface is rough and diffuses the light. (b) A mirror illuminated by many parallel rays reflects them in only one direction, because its surface is very smooth. Only the observer at a particular angle sees the reflected light.

Laws of Reflection Definition, Types, Formula, Uses, & FAQs
Laws of reflection: Reflection of waves obeys two laws. These are known as the laws of reflection. The incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal to the reflector at the point of incidence lie on the same plane. The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection, i.e., i = r. Reflection of Sound

Laws of Reflection of Light MarkhasColon
The law of reflection (in physics) states that when a light ray is incident on a plane surface, the incident ray, the reflected ray and the "normal" to the surface of the mirror all lie in the same plane. It also states that the angle the incident ray makes with the normal is equal to the angle that the reflected ray makes with the normal.

What are the laws of reflection?
The law of reflection is very simple: The angle of reflection equals the angle of incidence. The Law of Reflection The angle of reflection equals the angle of incidence. When we see ourselves in a mirror, it appears that our image is actually behind the mirror. This is illustrated in Figure 25.9.
What Is The Law Of Reflection Definition And A Simple Explanation
The law of reflection states: The angle of reflection, θr θ r, equals the angle of incidence, θi θ i . This law governs the behavior of all waves when they interact with a smooth surface, and therefore describe the behavior of light waves as well. The reflection of light is simplified when light is treated as a ray.